Allianz Issues Singapore Highlights from the Latest Global Wealth Report: The end of complacency
SINGAPORE,Sept. 28,2018 --
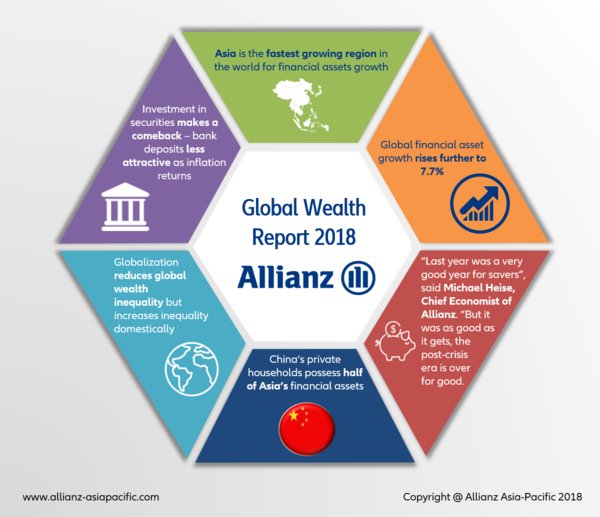
Global financial asset growth rises further to 7.7%
Financial assets of Singapore's private households increased by 8.9%,outpacing global growth
Globalization reduces global wealth inequality -- but increases domestic one
Today,Allianz unveiled the ninth edition of its "Global Wealth Report",which puts the asset and debt situation of households in more than 50 markets under the microscope.
Allianz Asia Global Wealth Report 2018
2017 was an exceptional year. Despite growing political tensions,it was an almost perfect year for investors. The economic recovery following the financial crisis culminated in a synchronous upturn around the globe and financial markets performed strongly,particularly equity markets.As a result,financial assets[1] of households rose significantly by 7.7%. Global gross financial assets increased to EUR 168 trillion.
"Last year was a very good year for savers," said Michael Heise,chief economist of Allianz. "But it was as good as it gets,the post-crisis era is over for good. Gone are the times when an extremely expansive monetary policy provided for a continuous and steady upward trend on financial markets. The signs are already worrying: Rising interest rates,trade conflicts,and increasingly populistic politics cause tensions and turbulences. The first month of this year gave already a bitter foretaste."
Singapore: Financial assets growth picked up
In 2017,financial assets of Singapore's households increased by 8.9%,which was not only a marked plus against 2016's 7.3% but also the highest growth rate since 2012. Growth drivers were securities with a plus of 12.6% and insurance and pensions assets,which were 10.9% higher than in the previous year. Insurance and pensions remained also the dominating asset class in Singapore's private households' portfolio,amounting to 48% of their total financial assets -- a fact that reflects not least the ageing of the society and the need for private old-age provision.
Despite the fact that loan growth picked up last year reaching 4.7% -- after a mere 2.4% and 2.5% in the two previous years -- the debt ratio remained stable at around 75%,much lower than,say,in South Korea (97.5%) or neighboring Malaysia (84.4). Net financial assets increased by 10.9%. With net financial asset per capita of EUR 90,650,Singapore came in 7th in the list of the richest markets (financial assets per capita,see table for the top 20) worldwide,rising one rung over the previous year and swapping places with Taiwan. In the regional ranking,Singapore came in second after Japan,relegating Taiwan to rank three. At the top of the list,Switzerland re-captured the top spot that it lost the year before to the US. In general,European markets did in 2017 better than in previous years; this,however,reflects first and foremost a stronger euro.
Industrialized nations catch up -- the US overtakes Mainland China
The years following the crisis were mainly characterized by relatively weak asset growth in industrialized compared to emerging markets. This also changed in 2017. The acceleration in growth was due solely to development in industrialized nations: while growth in these markets increased by more than one percentage point to 6.5%,in emerging markets it slackened by three percentage points to 12.9%. The growth differential between these two groups of markets was thus at its lowest level since 2005,at 6.5 percentage points. The average figure for the past decade was twice as high,at 13 percentage points. This contrasting development when it comes to growth in financial assets was largely due to the respective heavyweights,Mainland China (where growth slowed from 18.3% to 14%) and the US (where growth accelerated from 5.8% to 8.5%). In Asia (ex Japan) growth eased from 14.7% in 2016 to 12.2% in 2017. The US has thus overtaken Mainland China again in terms of absolute growth. In 2017,the US accounted for around 44% of global growth in gross financial assets of households,while Mainland China accounted for only about 25%. This ratio has averaged 26% vs. 35% over the last three years -- but with Mainland China coming out on top.
Debt growth accelerates further
Worldwide household liabilities rose by 6% in 2017. The growth rate was thus slightly above the previous year's level of 5.5%. In Asia (ex Japan),liability growth moved sideward,however on a high level,declining from 16.5% to 15.8% in 2017,due to the high credit demand in the region's emerging markets. Thanks to strong economic growth,the global debt ratio (liabilities as a percentage of GDP) increased only minimally to 64.3% (Asia ex Japan: 49.2%). These global averages naturally mask huge differences. In some markets debt levels and dynamics have reached critical figures in the last few years. "In the majority of analyzed markets,private debt dynamics are not worrisome," commented Michaela Grimm,co-author of the report. "However,in particular in Asia there are some markets -- Thailand,Malaysia,South Korea and Mainland China for example -- in which supervisory agencies should monitor the development very closely. In these markets,similarities to the credit excesses before the financial crisis cannot be overlooked." Despite the strong growth in liabilities,net financial assets i.e. the difference between gross financial assets and debt reached a new global record high of EUR 128.5 trillion at the close of 2017. This represents an increase of 8.3% compared with the previous year.
More participation thanks to globalization
The last two decades of rapid globalization have given rise to a new global wealth middle class,which included almost 1.1 billion people at the end of 2017. Fewer than half a billion people belonged to this group at the turn of the millennium,with just under half of them coming from Western Europe,North America or Japan. Today,these markets account for only a quarter of the global wealth middle class. In contrast,Mainland China's share has soared from just under 30% to over 50% in this period. The figures accompanying this success story are impressive: around 500 million Chinese people have moved up to join the ranks of the global wealth middle class since 2000,and over 100 million more can now even consider themselves part of the global wealth upper class. Thus today 62% of the global middle wealth class and 42% of the high wealth class are citizens of an Asian market.
More inequality in industrialized markets
The development of inequality in the national context,shows a very heterogeneous picture. Wealth distribution has improved in manymarkets since the turn of the millennium,but in many others it has deteriorated. The latter group includes a large number of industrialized markets,from the US to the euro crisis markets,and even Germany and Japan. The perception that the "old" industrialized nations in particular have been suffering in recent decades from a growing gulf between rich and poor therefore seems to match the reality in many cases. However,Singapore remained untouched from these developments,the distribution of wealth was more or less stable.
Investment in securities makes a comeback
There was a noticeable shift in investment behavior in 2017. After savers had largely ignored shares and investment funds in the post-crisis years,2017 saw significant inflows into this asset class. Its share last year reached almost a fifth of fresh funds,even more than in the years preceding the crisis. In the context of booming stock markets,this meant that securities enjoyed by far the strongest growth of all asset classes in 2017,increasing by 12.2% in total and representing over 42% of all savings at the end of 2017. This is followed in second place by receivables from insurance companies and pensions,which account for 29% of the asset portfolio and grew by 5.2% last year.
While investors rediscovered the capital markets,bank deposits fell out of favor with households around the globe. Only 42% of new investments went into banks,compared with 63% the year before. In absolute figures,this meant a drop of over EUR 390 billion. As a consequence,growth in deposits declined by two percentage points to 4.3% (share of asset portfolio almost 27%). "Savers finally recognized the signs of the times," said Kathrin Brandmeir,co-author of the report. "The withdrawal of love for bank deposits,particularly in the "old" industrialized markets,came not a second too early. Because inflation staged a return. Price increases in these markets tripled in 2017 -- albeit still on low level. As a result,losses in purchasing power of bank deposits shot up,too: They are estimated to add up to EUR 400 billion in 2017 alone."
A new indicator for the national distribution of wealth
To obtain a nuanced picture of national distribution in an international context,Allianz has introduced a new indicator in this report,the Allianz Wealth Equity Indicator (AWEI). Some of the results are surprising. Along with the "usual suspects" of the US,South Africa,Indonesia and the UK,markets where the distribution of wealth is relatively strongly distorted also include Denmark,Sweden and Germany. In Scandinavia this may be primarily due to high debt levels among large parts of the population; in Germany,the market's delayed reunification and the general shortage of capital-funded pension schemes play a crucial part. On the other hand,those markets where wealth distribution is relatively balanced include many eastern and western European markets,some of which are euro crisis markets such as Italy,Spain and Greece. Even if the last few years of crisis and austerity may have led to greater inequality in the last two markets in particular,they still have a relatively solid base to fall back on,as assets have traditionally been very widely distributed -- not least when it comes to real estate assets. Despite the recent worsening,Singapore ranks among the better performing markets in this ranking. "Our new wealth equity indicator shows clearly that we should be wary of drawing hasty or generalized conclusions," said Michael Heise. "Apart from the US,barely anymarket conforms to the cliche of wealth distribution that is already extremely distorted but is still getting worse. In most markets,shades of grey prevail."
Top 20 in 2017 by…
…netpercapitafinancialassets
...grosspercapitalfinancialassets
in EUR
y-o-y in %
rank
2000
in EUR
y-o-y in %
rank
2000
#1 Switzerland
173,990
6.7
1
#1 Switzerland
261,100
5.0
1
#2 USA
168,640
8.9
2
#2 USA
208,500
7.7
2
#3 Sweden
98,380
5.1
12
#3 Denmark
154,560
5.4
6
#4 Netherlands
95,880
-1.1
6
#4 Netherlands
143,950
-0.5
4
#5 Belgium
93,580
0.2
3
#5 Sweden
141,280
5.3
12
#6 Japan
92,000
4.7
4
#6 Australia
134,460
5.1
15
#7 Singapore
90,650
8.9
15
#7 Canada
127,470
5.5
8
#8 Taiwan
90,260
6.3
14
#8 Singapore
125,960
7.2
10
#9 Denmark
88,270
8.4
13
#9 Belgium
117,940
0.9
5
#10 Canada
87,390
6.3
8
#10 UK
114,890
2.4
7
#11NewZealand
83,570
2.0
9
#11 Japan
112,470
4.2
3
#12 UK
82,360
2.1
5
#12NewZealand
109,700
2.8
11
#13 Australia
72,080
5.4
18
#13 Taiwan
108,820
6.0
17
#14 Israel
68,710
3.9
10
#14 Norway
91,050
5.1
20
#15 France
59,100
4.1
11
#15 Israel
87,150
3.8
18
#16 Italy
58,610
4.9
7
#16 France
82,930
4.2
13
#17 Austria
53,980
3.5
17
#17 Ireland
79,250
2.2
14
#18 Germany
52,390
5.5
19
#18 Austria
75,460
3.0
19
#19 Ireland
47,440
5.9
16
#19 Italy
74,240
4.5
9
#20 Finland
30,230
4.8
20
#20 Germany
73,630
4.8
16
#21SouthKorea
30,220
8.2
25
#22SouthKorea
55,960
7.8
25
#30MainlandChina
13,550
11.7
40
#30MainlandChina
17,220
13.5
41
#35 Malaysia
8,350
10.4
27
#32 Malaysia
15,770
7.1
28
#44 Thailand
4,330
7.5
38
#41 Thailand
8,790
5.9
35
#52 Indonesia
650
11.2
48
#52 Indonesia
1,160
9.7
48
You can find the study onAllianz's homepage:
https://www.allianz.com/en/economic_research/ in the Publications/Specials section.
An interactive world map on households' assets and liabilities can be found here:
https://www.allianz.com/en/economic_research/research_data/interactive-wealth-map
ABOUT ALLIANZ
The Allianz Group is one of the world's leading insurers and asset managers with more than 86million retail and corporate customers. Allianz customers benefit from a broad range of personal and corporate insurance services,ranging from property,life and health insurance to assistance services to credit insurance and global business insurance. Allianz is one of the world's largest investors,managing over 650billion euros on behalf of its insurance customers while our asset managers Allianz Global Investors and PIMCO manage an additional 1.4trillion euros of third-party assets. Thanks to our systematic integration of ecological and social criteria in our business processes and investment decisions,we hold the leading position for insurers in the Dow Jones Sustainability Index. In 2017,over 140,000employees in more than 70markets achieved total revenue of 126billion euros and an operating profit of 11billion euros for the group.
These assessments are,as always,subject to the disclaimer provided below.
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
The statements contained herein may include prospects,statements of future expectations and other forward-looking statements that are based on management's current views and assumptions and involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties. Actual results,performance or events may differ materially from those expressed or implied in such forward-looking statements.
Such deviations may arise due to,without limitation,(i) changes of the general economic conditions and competitive situation,particularly in the Allianz Group's core business and core markets,(ii) performance of financial markets (particularly market volatility,liquidity and credit events),(iii) frequency and severity of insured loss events,including from natural catastrophes,and the development of loss expenses,(iv) mortality and morbidity levels and trends,(v) persistency levels,(vi) particularly in the banking business,the extent of credit defaults,(vii) interest rate levels,(viii) currency exchange rates including the EUR/USD exchange rate,(ix) changes in laws and regulations,including tax regulations,(x) the impact of acquisitions,including related integration issues,and reorganization measures,and (xi) general competitive factors,in each case on a local,regional,national and/or global basis. Many of these factors may be more likely to occur,or more pronounced,as a result of terrorist activities and their consequences.
NO DUTY TO UPDATE
The company assumes no obligation to update any information or forward-looking statement contained herein,save for any information required to be disclosed by law.
[1]
Financial assets include cash and bank deposits,receivables form insurance companies and pension institutions,securities (shares,bonds and investment funds) and other receivables.
Photo - https://photos.prnasia.com/prnh/20180928/2251760-1